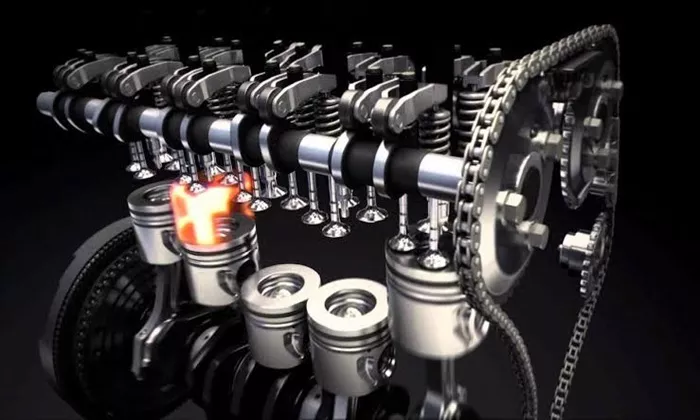
Spark-ignition (SI) engines, also known as gasoline engines, are a type of internal combustion engine that uses a spark plug to ignite the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. These engines are widely used in automobiles, motorcycles, and small machinery due to their efficiency, reliability, and relatively low emissions compared to other types of engines. The fundamental principle behind SI engines is the controlled combustion of a mixture of air and fuel, which is ignited by a spark at the optimal moment to produce power.
How Spark-Ignition Engines Work
The Four-Stroke Cycle
Spark-ignition engines typically operate on a four-stroke cycle, which includes the following stages:
Intake Stroke: The piston moves downward, creating a vacuum that draws in a mixture of air and fuel through the open intake valve.
Compression Stroke: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber.
Power Stroke: At the top of the compression stroke, the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing a rapid expansion of gases that forces the piston downward, generating power.
Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves upward again, expelling the burned gases from the combustion chamber.
The Role of the Spark Plug
The spark plug is a critical component of SI engines. It generates an electric spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture at the precise moment required for efficient combustion. The timing of the spark is crucial; if it occurs too early or too late, the engine’s performance and efficiency can be significantly compromised.
Advantages of Spark-Ignition Engines
High Efficiency and Power Output
SI engines are known for their high thermal efficiency and power output. The controlled combustion process allows for optimal energy extraction from the fuel, resulting in better fuel economy and higher performance compared to other types of engines.
Lower Emissions
Modern SI engines are equipped with advanced emission control systems, such as catalytic converters, which significantly reduce the amount of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. This makes them more environmentally friendly than many other types of internal combustion engines.
Smooth Operation
SI engines operate smoothly and quietly, providing a comfortable driving experience. The consistent and controlled combustion process minimizes vibrations and noise, making them ideal for use in passenger vehicles.
Challenges and Limitations of Spark-Ignition Engines
Knock and Pre-Ignition
One of the primary challenges faced by SI engines is the phenomenon known as “knock” or “pre-ignition.” This occurs when the air-fuel mixture ignites prematurely or unevenly, causing a knocking sound and potentially damaging the engine. To mitigate this issue, modern SI engines use high-octane fuels and advanced engine management systems.
Fuel Dependency
SI engines are designed to run on gasoline, which is a fossil fuel. This dependency on gasoline makes them vulnerable to fluctuations in fuel prices and availability. Additionally, the combustion of gasoline produces carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
Limited Efficiency at Low Loads
SI engines are less efficient at low loads, such as during idling or light cruising. This is because the throttle valve restricts the amount of air entering the engine, leading to higher pumping losses and reduced efficiency.
Innovations in Spark-Ignition Engines
Direct Injection Technology
One of the most significant advancements in SI engine technology is the development of direct injection systems. In these systems, fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber rather than the intake manifold. This allows for more precise control of the air-fuel mixture, resulting in improved efficiency, power output, and reduced emissions.
Variable Valve Timing
Variable valve timing (VVT) is another innovation that has enhanced the performance of SI engines. VVT systems adjust the timing of the intake and exhaust valves to optimize engine performance across a wide range of operating conditions. This results in better fuel economy, increased power, and lower emissions.
Turbocharging and Supercharging
Turbocharging and supercharging are techniques used to increase the power output of SI engines by forcing more air into the combustion chamber. This allows for a greater amount of fuel to be burned, resulting in higher power and torque. Turbocharged and supercharged engines are particularly popular in high-performance vehicles.
Conclusion
Spark-ignition engines have been a cornerstone of the automotive industry for over a century, providing reliable and efficient power for a wide range of applications. While they face challenges related to emissions and fuel dependency, ongoing innovations in technology and the adoption of alternative fuels are helping to address these issues. As the industry continues to evolve, SI engines are likely to remain a key component of the transportation landscape, albeit in increasingly advanced and environmentally friendly forms.