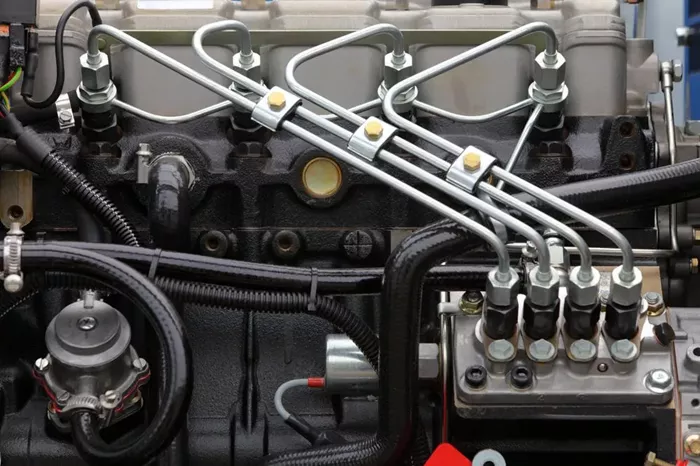
Fuel systems are a critical part of any internal combustion engine. Whether it’s a vehicle, generator, or industrial machine, the fuel system is responsible for delivering fuel from the storage tank to the engine in the correct amount, pressure, and condition. A well-functioning fuel system ensures optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and minimal emissions.
Understanding how fuel systems work is important not only for mechanical engineers and technicians but also for everyday users and fleet operators. This article breaks down the essential components, types, functions, and maintenance practices associated with fuel systems.
What Is a Fuel System?
A fuel system is a network of components that stores and delivers fuel to an engine. The system regulates the fuel’s flow and pressure while ensuring it is clean and vaporized before combustion. It plays a vital role in determining how efficiently the engine runs.
Modern fuel systems vary in design depending on the engine type and the fuel used—gasoline, diesel, biodiesel, ethanol, or renewable diesel. Regardless of the fuel type, the primary function remains consistent: efficient fuel delivery.
Key Components of Fuel Systems
Fuel Tank
The fuel tank is the reservoir where fuel is stored. Tanks are usually made of plastic or metal and vary in size based on the vehicle or equipment. In advanced systems, tanks may have internal baffles to reduce fuel slosh and sensors to monitor fuel levels and temperature.
Fuel Pump
Fuel pumps draw fuel from the tank and push it through the fuel lines to the engine. Two major types are:
- Mechanical Pumps: Typically used in older carburetor-based engines.
- Electric Pumps: Common in modern fuel-injected engines; they offer consistent pressure and control.
Fuel Filter
The fuel filter removes impurities and debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine. Clean fuel ensures better combustion and prevents damage to injectors or carburetors. Filters should be replaced regularly to avoid clogging.
Fuel Injectors or Carburetor
- Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold in a controlled manner.
- Carburetors: Mix fuel with air before it enters the engine. Though largely replaced by injectors, they are still found in some older models and small engines.
Fuel Lines
These are the pipes or hoses that carry fuel from the tank to the engine. Fuel lines must resist pressure, corrosion, and chemical degradation. High-performance fuel systems use reinforced or stainless-steel braided lines.
Pressure Regulator
This component maintains a steady fuel pressure, essential for proper engine operation. It ensures that the injectors or carburetor receive fuel at the required pressure level.
Sensors and Control Units
Modern systems include oxygen sensors, fuel pressure sensors, and electronic control units (ECUs) that monitor and adjust fuel flow for maximum efficiency and reduced emissions.
Types of Fuel Systems
Fuel systems can be categorized based on the fuel type and delivery method. Each has its advantages, design features, and maintenance requirements.
Gasoline Fuel Systems
These systems are commonly found in passenger vehicles. They are designed for cleaner combustion and usually feature high-pressure injectors and catalytic converters.
Key features:
- Lightweight components
- High-voltage spark ignition
- Fuel injection (multi-point or direct)
Diesel Fuel Systems
Diesel systems differ significantly due to their high compression ignition. They use heavy-duty components and deliver fuel at much higher pressures.
Key features:
- Direct injection
- Common rail or unit injector systems
- Turbocharging for efficiency
Biodiesel and Renewable Diesel Systems
These alternative fuels can be used in diesel engines with little or no modification. However, biodiesel can degrade rubber components and may require upgraded seals and filters.
Benefits:
- Lower carbon footprint
- Compatibility with existing infrastructure
- Renewable source material
Hybrid Fuel Systems
Hybrid systems combine internal combustion engines with electric motors. Though they reduce fuel consumption, the internal fuel system still plays a crucial role in engine performance.
Fuel Delivery Systems: Carburetor vs. Fuel Injection
Carburetor Systems
Carburetors use suction created by the engine’s intake air to draw and mix fuel. They are mechanically simple but less efficient.
Pros:
- Easy to repair
- Low cost
Cons:
- Poor fuel economy
- Inaccurate fuel-air mixture
Fuel Injection Systems
Fuel injectors deliver precise amounts of fuel directly into the engine. They are controlled by sensors and ECUs, ensuring optimized combustion.
Pros:
- Higher efficiency
- Better emissions control
Cons:
- More complex
- Costly repairs
Fuel System Maintenance
Maintaining your fuel system is crucial for engine longevity, performance, and safety. Poor maintenance can lead to fuel starvation, engine knocking, poor fuel economy, and even fires.
Regular Inspections
Routine checks help spot wear and tear in fuel lines, filters, and pumps. Look for signs of leaks, cracks, or unusual noises.
Filter Replacement
Dirty filters restrict fuel flow and increase pump stress. Follow the manufacturer’s replacement schedule—usually every 20,000 to 40,000 miles for vehicles.
Fuel Additives
Fuel system cleaners help remove carbon deposits, varnish, and moisture. Use them periodically to maintain injector performance and reduce emissions.
Diagnosing Problems
Common symptoms of fuel system issues include:
- Engine misfires
- Difficulty starting
- Reduced power
- Poor acceleration
- Increased fuel consumption
Use onboard diagnostics (OBD) or take your vehicle to a service center for inspection.
Importance of Fuel System Efficiency
An efficient fuel system not only improves performance but also reduces harmful emissions and fuel consumption. For industries like transportation, construction, and logistics, this translates to lower operational costs and environmental impact.
Benefits of fuel system efficiency:
- Enhanced combustion
- Extended engine life
- Lower emissions
- Better throttle response
- Improved mileage
Innovations in Fuel System Technology
Direct Injection Systems
These systems deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber at high pressure. They improve fuel atomization, leading to cleaner and more powerful combustion.
Variable Fuel Pressure Systems
Some modern vehicles adjust fuel pressure depending on driving conditions. This enhances fuel efficiency and performance under load.
Advanced Fuel Filters
Nano-fiber fuel filters are being developed to capture smaller contaminants without restricting fuel flow.
Integration with ECU and Telematics
Smart fuel systems communicate with engine control units and telematics platforms to provide real-time fuel data. Fleet managers can monitor consumption patterns and detect issues early.
Fuel Systems in Industrial and Marine Applications
Industrial Equipment
Bulldozers, excavators, and generators require robust fuel systems. These systems are designed to operate under extreme conditions and with minimal downtime.
Challenges:
- Dust and debris
- Vibration
- Long operating hours
Solutions:
- Heavy-duty filters
- Redundant fuel lines
- Pressure stabilizers
Marine Fuel Systems
Boats and ships have unique fuel system designs due to moisture, corrosion, and long operational hours.
Components include:
- Water separators
- Anti-siphon valves
- Fuel polishing systems
Marine diesel systems must comply with MARPOL regulations, which govern fuel quality and emissions.
Fuel System Regulations and Safety Standards
Fuel systems must comply with environmental and safety regulations such as:
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) standards
- CARB (California Air Resources Board) guidelines
- ISO and SAE standards for component design
Safety regulations cover:
- Leak prevention
- Fire resistance
- Emission limits
- System pressure ratings
Conclusion
Fuel systems are more than just pipelines for fuel delivery—they are intelligent, highly engineered systems that influence efficiency, emissions, and engine reliability. Understanding each component and how it works together allows for better maintenance, innovation, and operational performance.
From conventional gasoline engines to advanced marine and industrial systems, fuel system technology continues to evolve. Staying informed helps individuals and businesses make better decisions in terms of maintenance, upgrades, and energy use.